Realtime AI Voice Changer Explained: How It Works
Imagine speaking into a microphone and instantly sounding like a different person, a fictional character, or even a perfectly branded corporate voice, all without noticeable delay. This is no longer science fiction. Realtime AI voice changers are rapidly reshaping how humans interact with technology, each other, and digital environments. From gaming and livestreaming to customer support and virtual meetings, the ability to transform a voice in real time has become both a technical breakthrough and a practical business tool.
Yet for many people, the underlying question remains unanswered: how does a realtime AI voice changer actually work? Is it just an advanced audio filter, or something far more complex? In this in-depth article, we unpack the technology behind realtime AI voice changers step by step, separating hype from reality and giving you a clear, expert-level understanding of the systems powering this fast-growing AI application.
What Is a Realtime AI Voice Changer?
A realtime AI voice changer is an artificial intelligence system that modifies a person’s voice instantly while they are speaking, transforming vocal characteristics such as pitch, tone, timbre, and speaking style, without altering the spoken words themselves. Unlike traditional voice effects that rely on simple signal manipulation, AI-based voice changers use deep learning models trained on human speech to generate natural-sounding results.
The key differentiator lies in the word realtime. The system must capture audio, analyze it, transform it, and output a new voice within milliseconds. If latency exceeds roughly 30–50 milliseconds, human listeners begin to notice delays, which can break immersion in live conversations, games, or broadcasts.
Realtime vs Offline AI Voice Processing
To understand why realtime voice changing is challenging, it helps to compare it with offline AI voice processing.
- Offline processing: Audio is recorded first, then processed using complex models. This allows for higher accuracy but introduces seconds or minutes of delay.
- Realtime processing: Audio is processed frame by frame as it is spoken, demanding highly optimized models and efficient hardware.
Offline AI voice cloning, for example, can take hours to generate a voice model from recorded samples. Realtime AI voice changers, by contrast, rely on pre-trained models and lightweight inference pipelines that prioritize speed without sacrificing too much quality.
Why Realtime AI Voice Changers Are Gaining Massive Popularity
The surge in realtime AI voice changer adoption is closely tied to how humans communicate today. Live digital interaction has become the default rather than the exception. According to a 2023 report by Statista, over 27% of global internet users participate in live streaming or online gaming weekly, environments where voice identity plays a central role.
At the same time, businesses are under pressure to deliver faster, more personalized, and more scalable communication. AI-powered voice transformation offers a compelling solution by combining automation with human-like interaction.
Key Industries Using Realtime AI Voice Technology
Realtime AI voice changers are no longer niche tools. They are being actively deployed across multiple sectors:
- Gaming and live streaming: Streamers use AI voice changers to protect privacy, role-play characters, or entertain audiences.
- Customer support and call centers: Companies standardize brand voice and enable multilingual support using AI voice transformation.
- Content creation: Podcasters, YouTubers, and voice actors reduce production costs while expanding creative possibilities.
- Education and training: Instructors simulate different speaking styles or anonymize voices during live sessions.
- Accessibility: AI voice technology supports users with speech impairments by converting input into clearer or alternative voices.
As Dr. Alan Black, a leading speech synthesis researcher, notes: Realtime speech transformation is not just about entertainment. It represents a fundamental shift in how voice becomes a programmable interface.
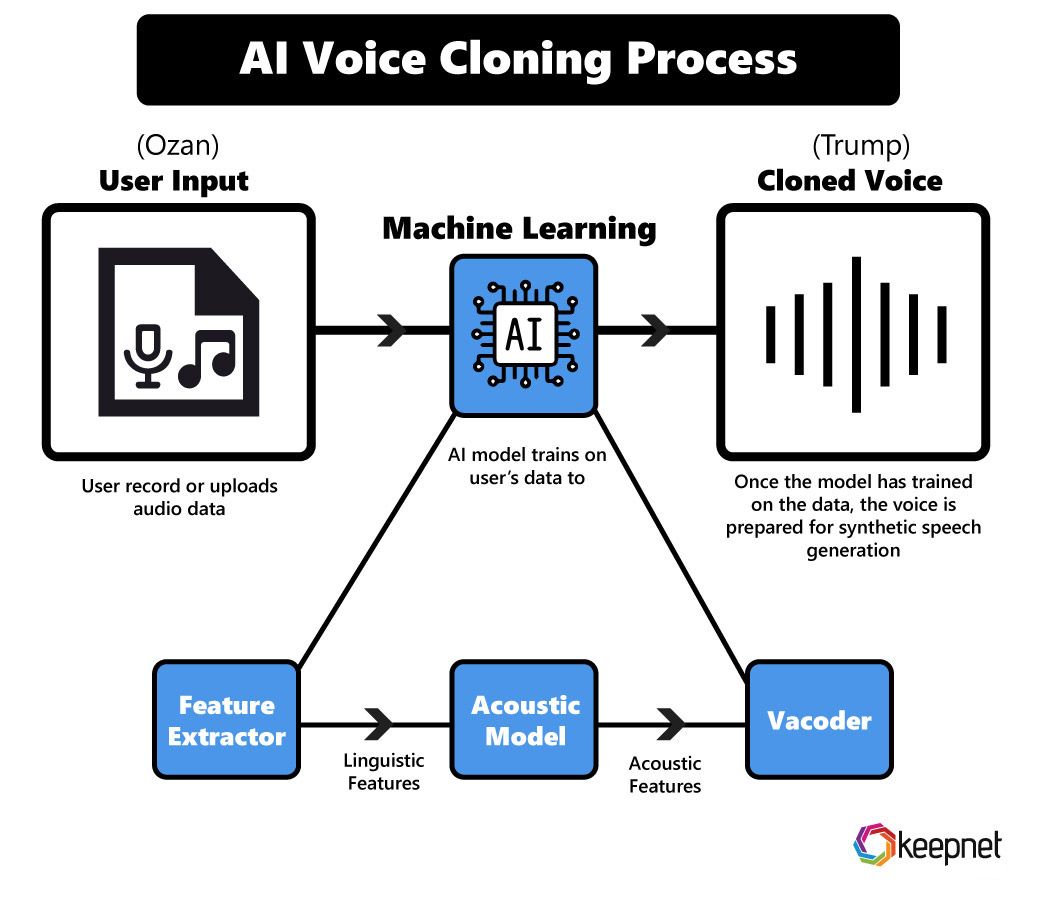
How Realtime AI Voice Changers Work (Step-by-Step)
Despite the impressive results, the internal workflow of a realtime AI voice changer follows a logical and repeatable pipeline. Understanding this pipeline is essential for evaluating voice quality, latency, and reliability.
Step 1: Voice Input Capture
The process begins with capturing the speaker’s voice through a microphone. The analog sound waves are converted into a digital signal using an audio interface. Two technical parameters matter most at this stage:
- Sampling rate: Commonly 16 kHz or 44.1 kHz, determining how frequently the audio signal is measured.
- Bit depth: Typically 16-bit or 24-bit, affecting dynamic range and clarity.
Higher-quality input audio significantly improves the final AI-generated output. Poor microphones or background noise introduce artifacts that even advanced AI models struggle to remove in real time.
Step 2: Audio Pre-Processing
Before AI models can analyze speech, the raw audio undergoes pre-processing. This stage ensures the signal is clean, consistent, and suitable for real-time inference.
- Noise reduction: Filters remove background sounds such as keyboard typing or fan noise.
- Voice activity detection (VAD): The system detects when the user is speaking to avoid unnecessary processing.
- Normalization: Audio levels are adjusted to maintain consistent volume.
These steps may seem minor, but they directly affect latency and output quality. Efficient pre-processing pipelines are a hallmark of professional-grade realtime AI voice changers.
Step 3: Feature Extraction
Once pre-processed, the audio signal is transformed into numerical representations that AI models can understand. This is known as feature extraction, and it is one of the most critical stages in realtime voice transformation.
Instead of working with raw waveforms, AI systems analyze features such as:
- Mel-spectrograms: Visual representations of sound frequency over time, aligned with human hearing.
- Pitch and prosody: Information about intonation, rhythm, and stress.
- Formants: Frequency bands that define vocal identity.
These features allow the AI to separate what is being said from who is saying it. This separation is the foundation of realtime voice changing.

Research published in Applied Sciences highlights that mel-spectrogram-based processing remains the most effective approach for balancing speed and accuracy in realtime voice systems.
Common Audio Features Used in AI Voice Conversion
Most modern realtime AI voice changers rely on a combination of well-established speech features:
- MFCCs (Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients): Compact representations of the speech spectrum.
- Prosodic features: Capturing emotion and speaking style.
- Spectral envelopes: Preserving linguistic content while allowing voice transformation.
At this point in the pipeline, the system has effectively translated human speech into a structured, machine-readable format. In the next stage, neural networks take over to perform the actual voice transformation, a process we will explore in the second half of this article.
Step 4: Neural Network Voice Transformation
This is the core intelligence layer of a realtime AI voice changer. Once speech features are extracted, they are passed into deep learning models trained to transform the speaker’s vocal identity while preserving linguistic content. Unlike simple pitch-shifting algorithms, neural networks understand speech at a structural level.
Modern realtime AI voice changers typically rely on encoder–decoder architectures. The encoder compresses input features into a latent representation that captures what is being said. The decoder then reconstructs the voice using characteristics of a target speaker or style.
Popular AI Models Behind Realtime Voice Changers
- Autoencoders: Efficient models that learn compact voice representations and are widely used for low-latency transformation.
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks): Improve realism by training a generator and discriminator in parallel.
- Transformers: Capture long-range dependencies in speech, improving naturalness and expressiveness.
- Diffusion models: An emerging approach offering superior quality, though still challenging for strict realtime constraints.
According to research published on ResearchGate, modular neural network architectures allow different components, such as pitch control and timbre modeling, to operate independently, improving both speed and scalability.
How AI Preserves Speech Content While Changing Voice
One of the most impressive capabilities of a realtime AI voice changer is its ability to maintain speech clarity while altering vocal identity. This is achieved through speaker embedding vectors. These vectors represent vocal traits separately from language content.
By swapping or modifying speaker embeddings during inference, the AI generates a new voice without changing pronunciation, pacing, or word choice. This technique is what allows live voice conversion to sound coherent and human-like.
Step 5: Real-Time Synthesis and Audio Output
After transformation, the AI-generated voice must be converted back into an audible waveform. This task is handled by a neural vocoder, such as WaveNet-inspired or HiFi-GAN-based systems optimized for speed.
The synthesized audio is streamed directly to the output device, whether that is a game, streaming software, conferencing tool, or call center system.
Latency Optimization Techniques
- Model compression: Reducing model size without sacrificing quality.
- Edge processing: Running inference locally to avoid network delays.
- GPU and AI accelerator usage: Leveraging hardware acceleration.
Well-optimized realtime AI voice changers typically achieve end-to-end latency below 40 milliseconds, a threshold considered imperceptible in live conversations.
Realtime AI Voice Changer vs AI Voice Cloning
Although often confused, realtime AI voice changers and AI voice cloning serve different purposes. Understanding the distinction is crucial when selecting an AI voice solution.
| Aspect | Realtime AI Voice Changer | AI Voice Cloning |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Live voice transformation | Voice replication from samples |
| Latency | Milliseconds | Seconds to minutes |
| Training Data | Pre-trained models | Custom voice recordings |
| Best For | Streaming, calls, gaming | Content production, narration |
In short, realtime AI voice changers prioritize speed and flexibility, while voice cloning focuses on accuracy and replication.
Real-World Use Cases of Realtime AI Voice Changers
Gaming and Live Streaming
Gamers and streamers use realtime AI voice changers to protect privacy, role-play characters, or enhance entertainment value. Platforms like Twitch and YouTube Live have accelerated adoption, as voice identity becomes part of a creator’s brand.
Business and Customer Support
Call centers increasingly deploy AI voice technology to standardize brand tone, enable multilingual interactions, and reduce agent fatigue. A 2024 Gartner report predicts that over 40% of customer service interactions will involve AI-assisted voice systems by 2026.
Content Creation and Education
Educators and creators use realtime AI voice changers to anonymize speakers, simulate scenarios, or adapt content for different audiences without re-recording.
Benefits and Limitations of Realtime AI Voice Changers
Key Benefits
- Instant voice transformation with minimal delay
- Lower production and staffing costs
- Scalable across platforms and use cases
Current Limitations
- Hardware dependency for best performance
- Potential artifacts under poor audio conditions
- Ethical and regulatory challenges
Ethical, Legal, and Privacy Considerations
As powerful as realtime AI voice changers are, they raise important ethical questions. Voice is a biometric identifier, and misuse can lead to impersonation or fraud.
Responsible AI platforms emphasize consent, data security, and transparency. Regulatory frameworks in regions such as the EU are increasingly addressing AI-generated media, underscoring the importance of choosing trustworthy providers.
How to Choose the Right Realtime AI Voice Changer
Evaluation Criteria
- Voice naturalness and stability
- Latency and system requirements
- Language and accent support
- Transparent pricing and licensing
Platforms like ai.duythin.digital help users compare AI voice solutions objectively, saving time and reducing risk by offering expert reviews and feature breakdowns.
The Future of Realtime AI Voice Technology
The future of realtime AI voice changers points toward emotion-aware voices, near-zero latency, and seamless integration with virtual avatars and metaverse environments. Advances in efficient neural architectures will continue to blur the line between human and synthetic speech.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is a realtime AI voice changer legal?
Yes, when used with consent and for legitimate purposes. Laws vary by region, so compliance is essential.
Can realtime AI voice changers sound completely natural?
High-end systems already approach human-level realism, especially under controlled audio conditions.
Do realtime AI voice changers require powerful hardware?
Performance improves with better hardware, but optimized models can run on modern consumer devices.
Conclusion
Realtime AI voice changers represent a major milestone in human–computer interaction. By combining advanced speech processing, neural networks, and low-latency engineering, these systems enable live voice transformation that is practical, scalable, and increasingly realistic.
Whether you are a business leader, creator, or technology enthusiast, understanding how realtime AI voice changers work empowers you to make smarter decisions in an AI-driven world.
Take the Next Step
If you are exploring AI voice solutions for business or personal use, visit ai.duythin.digital to access in-depth reviews, feature comparisons, and transparent pricing from Vietnam’s leading AI community. Save time on research and choose AI tools with confidence.